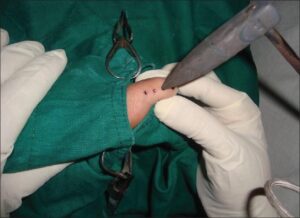
Agnikarma, also known as cauterization, is a therapeutic procedure in Ayurveda that involves the application of heat to the surface or deeper tissues of the body to manage various afflictions. It is considered a superior para-surgical procedure aimed at providing relief from pain and promoting healing. Here’s an overview of Agnikarma:
Tools of Cauterization:
Tools of cauterization are materials subjected to heat and used for therapy in different conditions. The choice of material depends on the disease status and the depth of tissue involvement. Some common tools of cauterization include Pippali (Piper longum), Aja Shakrit (feces of Goat), Godanta (Teeth of Cow), Shara (Arrow), Shalaka (Probes), Varti (Wicks), Suryakanta (Variety of stone), Loha (Iron), Swarna (Gold), Tamra (Copper), Kamsya (Bronze), Madhu (Honey), Guda (Jaggery), Vasa (Fat), Ghrita (Ghee), Taila (Oil), and Madhucchishta (Beeswax).
Procedure:
During Agnikarma therapy, heat is applied to the affected area using various methods, such as heated instruments, moxibustion (burning of specific herbs), or direct application of heat through specialized tools. The therapy is performed by trained practitioners who understand the principles of Ayurveda and the specific techniques involved in Agnikarma.
Indications:
Agnikarma therapy is indicated for a wide range of conditions, including but not limited to:
- Painful musculoskeletal conditions such as arthritis, joint stiffness, and muscle spasms
- Neurological conditions like sciatica and neuropathic pain
- Dermatological conditions such as warts, corns, and skin tags
- Inflammatory conditions like tendonitis and bursitis
- Certain gynecological and urological disorders
- Some respiratory conditions
Mechanism of Action:
The therapeutic effects of Agnikarma therapy are thought to be mediated through several mechanisms:
- Heat application stimulates blood circulation to the affected area, promoting the delivery of oxygen and nutrients and aiding in tissue repair.
- Heat induces vasodilation, which can help reduce inflammation and swelling.
- The application of heat may alter nerve conduction, leading to pain relief through mechanisms such as the gate control theory of pain.
- In some cases, Agnikarma therapy may also have a cauterizing effect, helping to remove abnormal tissue growths or lesions.
Contraindications:
While Agnikarma therapy can be beneficial for many individuals, there are certain contraindications to consider. It may not be suitable for individuals with:
- Acute inflammatory conditions with significant swelling and redness
- Open wounds or active infections in the area to be treated
- Sensory deficits or impaired circulation in the affected area
- Certain systemic conditions or underlying health concerns that may increase the risk of complications
Benefits:
- Provides relief from pain and discomfort associated with various conditions
- Promotes healing and tissue repair
- May reduce inflammation and swelling
- Can be tailored to individual patient needs and preferences
- Generally considered safe when performed by trained practitioners
Risks and Considerations:
While Agnikarma therapy is generally safe, there are some potential risks and considerations to be aware of, including:
- Risk of burns or tissue damage if not performed properly
- Possibility of adverse reactions or complications in certain individuals
- Need for proper assessment and diagnosis before initiating therapy
- Importance of seeking treatment from qualified practitioners with experience in Agnikarma techniques
In conclusion, Agnikarma therapy is a time-tested Ayurvedic treatment modality that offers relief from pain and promotes healing in various conditions. However, it is essential to approach this therapy with caution, ensuring proper assessment, diagnosis, and treatment by qualified practitioners to maximize its benefits and minimize risks.